Genetic-abnormality
If Previous Child or any family member has genetic problem such as Down’s syndrome, patau syndrome, metabolic disorders or any kind of hereditary illness which runs is family, can get solved by PGD & PGS technique .
Advanced IVF , ICSI-Embryo biopsy select almost 200 abnormal variant in embryo & offer genetically disease free healthy baby
PGD
What is PGD or preimplantation genetic diagnosis?
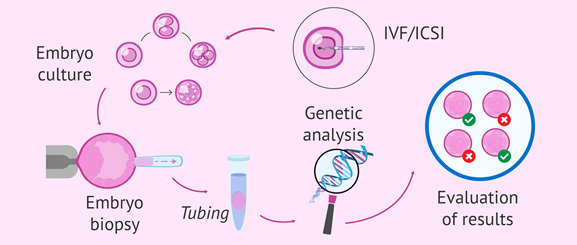
PGD is a technique that provides information about the gene make-up of the cells found in an embryo (a fertilized egg). An embryo biopsy removes about 3-8 cells from each day 5 embryo (a blastocyst), then cells are sent to a lab for testing. The embryo is usually frozen and implanted later. PGD can be used to identify approximately 2,000 inherited single gene disorders and is 98 percent accurate identifying affected and unaffected embryos.
Who benefits most from PGD?
PGD is generally used by couples with a family history of a serious or deadly disease who worry about passing it on to their offspring. PGD helps by looking for specific markers for a certain disease, for example, single gene disorders including cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anemia. It is also used when there’s a family history of sex-linked disorders including Fragile X syndrome and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Parents may also use PGD to find matching stem cells for other siblings in need of a bone marrow transplant.
PGS
What is PGS or preimplantation genetic screening?
PGS is used to determine whether the cells in an embryo contain the normal number of chromosomes, which is 46. After an embryo grows in the lab, it is usually biopsied on day 5 (blastocyst stage). A few embryo cells are then sent to an external lab which uses technology to count the number of chromosomes within each cell. Embryos with a normal number of chromosomes are “euploid” and those with an abnormal number are “aneuploid.” The purpose of PGS is to avoid transferring an abnormal embryo into the uterus.
Who benefits most from PGS?
All couples are at risk for having abnormal embryos. This risk increases significantly as a woman gets older. An abnormal embryo almost always fails to implant, or if it does, ends in a biochemical pregnancy (only hormone evidence of pregnancy), miscarriage, fetal death later in pregnancy, stillbirth or a baby with abnormalities.
Couples undergoing IVF may select PGS because they have severe male factor infertility, recurrent IVF failures, older age or a very large number of embryos. PGS can be used by those experiencing multiple miscarriages who may have different types of translocations where a piece of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome resulting in a gain or loss of a cell’s genetic material.
Use of PGS has grown rapidly because of support by many physicians and patients who want to transfer a normal embryo. Some estimates suggest PGS is used in nearly 35 percent of all IVF cases and predict it may soon be used in half of all cycles
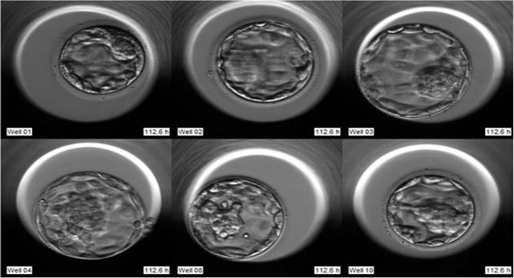
Embryo Time lapse techniques
Time-lapse technology (TLT) systems are used in some laboratories to facilitate embryo monitoring. In a TLT incubator, images of embryo development are recorded at regular intervals of 5–15 min.